Carrier Supra 650 Service Manual Page 20
- Page / 92
- Table of contents
- TROUBLESHOOTING
- BOOKMARKS
Rated. / 5. Based on customer reviews


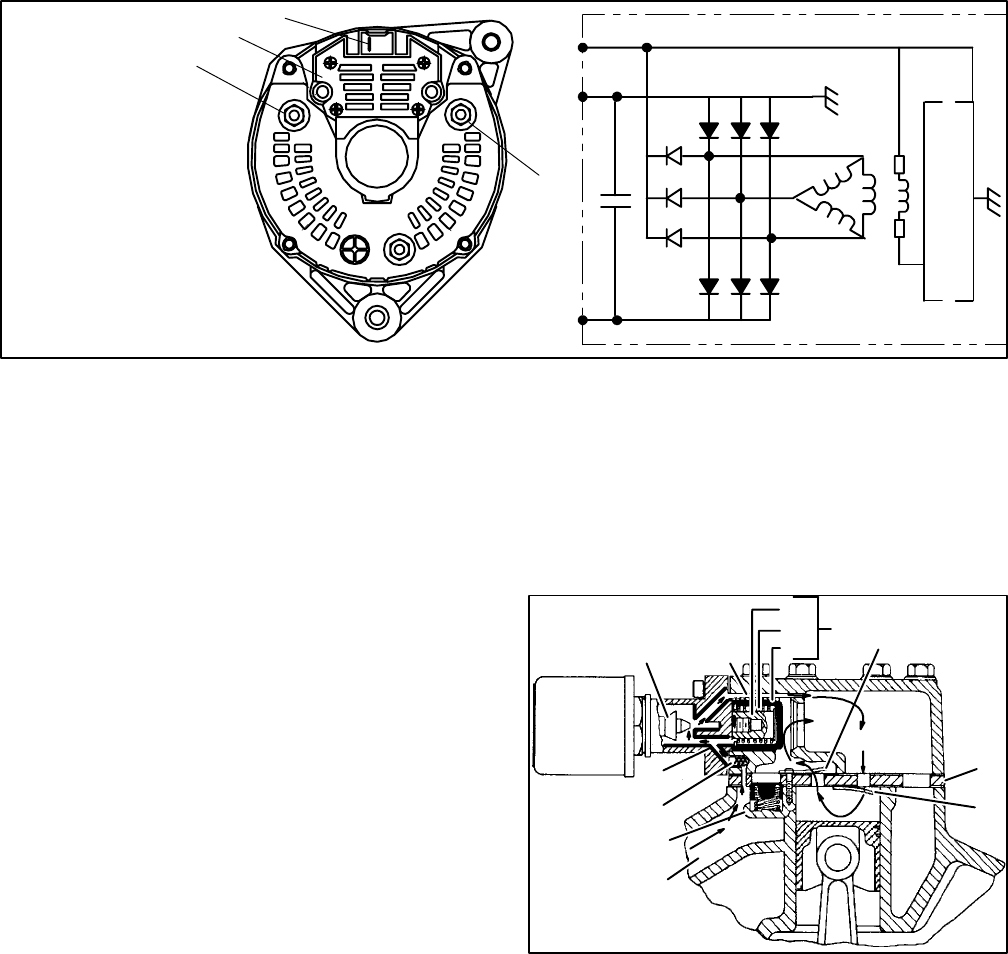
1--7
62--10828
1
L
B--
B+
2
3
4
1. Positive Output
Terminal
2. Regulator
3. 12vdc Test Lamp
Terminal
4. Ground Terminal
Figure 1-6. 70 Amp Alternator (P/N 30-60050-04)
1.3.2 Condensing Section Refrigeration System
The condensing section mounted refrigeration system
equipment includes the compressor, condenser/sub-
cooler, accumulator, defrost air switch, filter drier, re-
ceiver, hot gas (three way) valve, hot gas bypass valve
(except for 950) and compressor pressure regulating
valve.
a. Compressor
The compressor assembly includes the refrigerant com-
pressor, suction and discharge service valves, high
pressure switch, unloader(s) (850 and 950 only) and the
suction pressure transducer. The compressor draws
refrigerant gas from the evaporator and delivers it to the
condenser at an increased pressure. The pressure is
such that refrigerant heat can be absorbed by the sur-
rounding air at ordinary temperatures.
b. Compressor Unloader (850 and 950 Only) (Refer
to Section 3.1.7 for detailed information on unloader
temperature control)
The Supra 850 and 950 unit compressors are fitted with
one electric unloader valve. The capacity controlled cyl-
inder is easily identified by the solenoid which extends
from the side of the cylinder head. When the solenoid is
energized two cylinders are unloaded. The unloaded
cylinders operate with little or no pressure differential,
consuming very little power. A description of unloader
operation is provided in the following steps.
Unloaded Operation
Pressure from the discharge manifold (Figure 1-7, item
15) passes through the strainer (9) and bleed orifice (8)
to the back of the piston bypass valve (7). Unless bled
away, this pressure would tend to close the piston (6)
against the piston spring (5) pressure.
With the solenoid valve (1) energized the solenoid valve
stem (2) will open the gas bypass port (3).
Refrigerant pressure will be bled to the suction manifold
(10) through the opened gas bypass port . A reduction in
pressure on the piston bypass valve will take place be-
cause the rate of bleed through the gas bypass port is
greater than the rate of bleed through the bleed orifice
(8).
When the pressure behind the piston has been reduced
sufficiently, the valve spring will force the piston bypass
valve back, opening the gas bypass from the discharge
manifold to the suction manifold.
Discharge pressure in the discharge manifold will close
the discharge piston check valve assembly (14) isolat-
ing the compressor discharge manifold from the individ-
ual cylinder bank manifold.
The unloaded cylinder bank will continue to operate fully
unloaded until the solenoid valve control device is de--
energized and the gas bypass port is closed.
10
11
12
13
4
6
5
15
14
1
9
2
3
8
7
1. Solenoid
V
alve
2. Valve Stem
3. Gas Bypass Port
4. Spring Guide
5. Spring
6. Piston
7. Piston Bypass Valve
8. Bleed Orifice
9. Strainer
10.Suction Manifold
11. Cylinder Discharge
Valve
12. Valve Plate
13. Cylinder Suction
Valve
14. Discharge Piston
Check Valve
Assembly
15. Discharge Manifold
Figure 1-7. Cylinder Head -- Unloaded
- OPERATION & SERVICE 1
- OPERATION AND 2
- SERVICE MANUAL 2
- TABLE OF CONTENTS 3
- LIST OF ILLUSTRATIONS 8
- LIST OF TABLES 9
- SAFETY SUMMARY 10
- SECTION 1 14
- DESCRIPTION 14
- 20 35° F 15
- -20 35° F 32
- SECTION 3 43
- SUPRA 550/650/750/850 50
- CONTINUOUS MODE 50
- START / STOP MODE 51
- SUPRA 950 52
- SECTION 4 54
- 62--10828 75
- Table 4-4 Configuration Table 75
- 62--108284--23 76
- SECTION 5 79
- TROUBLESHOOTING 79
- SECTION 6 85
- CONNECT TO OVERLOAD RELAY 87
 (29 pages)
(29 pages)







Soy mecánico mantenedor. Necesito manuales técnicos